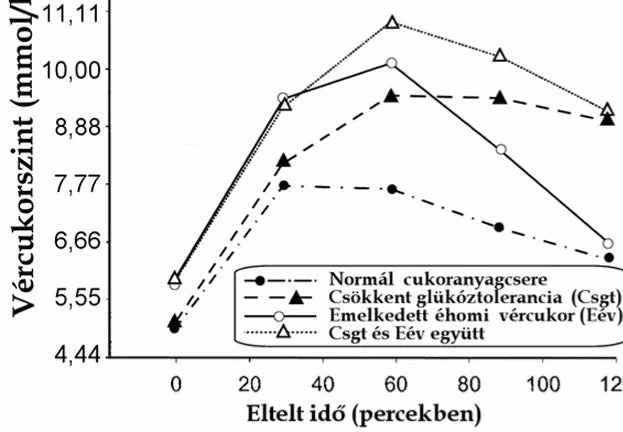
Normal-disordered sugar metabolism
Allulose StoreThe graph shows the blood sugar curve of four types of sugar metabolism states as a function of time (mmol/l, min)
Normal sugar metabolism
The lowest blood sugar level is seen on an empty stomach (0 minutes), then it rises rapidly after a glucose load, but returns to baseline relatively quickly, indicating the body's good insulin response and glucose utilization.
Impaired glucose tolerance (IGT)
Here, the rise in blood sugar levels is greater, especially around 60 minutes after exercise, but eventually returns close to the initial value – this is a slight disturbance in glucose processing, but it is still reversible.
Elevated fasting blood sugar (FBS)
The curve starts with a higher blood sugar level even on an empty stomach, and after exercise it reaches a higher peak than normal. This is a sign of early metabolic disorder, when the decrease in blood sugar, especially at night, is insufficient.
Csgt and Eév together
In this case, both the fasting value and the peak after a glucose load are higher than the previous ones, and blood sugar levels return to baseline more slowly.
This is the most severe disorder of the four, indicating significant insulin resistance and impaired glucose regulation.
The point
The greater the increase in blood sugar levels, and the higher the fasting and recurrent values, the more severe the sugar metabolism disorder, which indicates the risk of developing diabetes.

